---
description: "Compare Cypress, Selenium, and Playwright to find the best automated testing tool for your frontend web applications. Discover the strengths and weaknesses of each tool."
---
<h1> Cypress vs Selenium vs Playwright: The Best Automated-Testing Tool</h1>
<p>In today's ever-changing technological environment, developers and testers are under constant pressure to design, test and deliver fully functional software products in the shortest amount of time possible. As a result, the importance of using Automated tools for testing cannot be overemphasized, not just for testers but also for developers. Given that Manual testing is not a completely infallible approach to testing software, Most organisations utilize Automation testing because it allows them to thoroughly test a software product with limited time and resources. Automation testing differs from Manual testing because Manual testing involves the presence of an human tester interacting with a system or software in order to identify bugs, while Automation testing involves the usage of Automated testing tools and scripts to verify that a particular software is performing up to standard. Automated testing tools have two major components: a Test runner and a Tracking agent. The test runner runs the test from a command (or button click) while the tracking agent keeps track of passing and failing tests. These Automated testing tools apply to different software testing types which include unit, integration, end-to-end (e2e) testing,among others.
<br><br>
There are various software applications written in different programming languages and choosing the most suitable Automated testing tool for each of these applications can be difficult due to the availability of various Automated testing tools on the market. This article aims to compare three of the most used Automated testing tools namely: Cypress, Playwright and Selenium using metrics such as Browser Support, Language Support, Ease of setup, and Performance. This comparison will serve as a guide in choosing the tool that best suits your testing needs. </p>
## What is Automated Testing and Why is it Important
<p>Automated testing is a testing technique that involves the use of software tools in executing test cases. It often involves test cases written in scripting languages such as Python, JavaScript, or Lua. The scripts are written to test the different functionalities of a piece of software.
Automated testing can be seen as a process of Automating Manual test cases, that is, using software tools to execute test cases that would have been executed Manually. The goal of Automated testing is to reduce the amount of Manual work involved in test execution, leading to higher test coverage.
Below are some benefits of Automated testing:
* **Elimination of human error**: Humans are naturally predisposed to making mistakes and while this fact is known all over the world, the field of testing requires a level of perfection that might be humanly impossible, due to the inability of humans to carry out tasks perfectly at all times, Automated testing is very important because it reduces the likelihood and impact of human errors.
> **Please Note**: Humans are still very involved in the process of Automated testing. For example, an human tester is the one responsible for writing and maintaining Automated test scripts, but since Automated testing allows testers to run scripts repetitively without the need to re-write it, the problem of human error would be less likely to occur.
* **Speed and Efficiency**: Automated testing is much faster than manual testing because an Automated test script runs at machine speed which in turn leads to faster feedback. Automated testing also supports parallel testing which allows multiple test scripts to run simultaneously across different environments which also speeds up feedback time.
* **Increased Coverage**: It can be very tiring on the part of the tester to execute large amounts of test cases, and in certain scenarios some test cases are overlooked because they are considered unimportant, this can lead to a major issue but through the use of Automated testing, large number of test cases can be executed under a short period of time.
> **Please note**: Automation testing is not a replacement for manual testing so it doesn't eliminate the need for human testers, rather it creates an avenue for human testers to carry out tests with testing tools.
<h3> Use-Cases of Automated Testing </h3>
* Cross-browser testing
* Load and performance testing
* Automating unit, integration, and end-to-end tests
## Comparing Cypress, Selenium, and Playwright as Automated Testing Tools
<p>Now, let's compare Cypress, Selenium, and Playwright based on Browser support, Ease of setup, Ease of scripting, Performance and Speed.</p>
### Choosing the best Automated testing tool based on Browser support
<p>Browser support refers to the ability of a certain website or web app to function consistently on different web browsers (Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Safari, and Microsoft Edge). If your favourite Automated testing tool can work across major browsers, you can have peace of mind that your app works no matter the browser choice of your users. The essence of considering browser support is that cross-browser testing is one of the major tests carried out by testers and devs. Now, let's take a look at all three Automated testing tools in terms of browser support:
<p><strong>Cypress:</strong> Cypress supports major browsers like Chromium and Firefox. <a href="https://docs.cypress.io/guides/guides/launching-browsers#WebKit-Experimental">Though it has experimental support for Safari</a> which means that not all features will work properly. Asides from this, it has good support on Chrome, Firefox, and Edge. It can run tests across multiple browser versions directly from the Cypress test runner, which makes it convenient to run tests on older browser versions, maintained versions, and unreleased versions.</p>

**Selenium**: Selenium supports popular web browsers including Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Safari, Microsoft Edge, and Internet Explorer (Edge IE mode). It achieves this through the Selenium webdriver which acts as a bridge between test scripts and a chosen browser. There is no single webdriver, as each browser type has its own webdriver. Available webdrivers include:
- [ChromeDriver](https://chromedriver.chromium.org/downloads) for Google Chrome.
- [GeckoDriver](https://firefox-source-docs.mozilla.org/testing/geckodriver/index.html) for Mozilla Firefox.
- [EdgeDriver](https://developer.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-edge/tools/webdriver/) for Microsoft Edge.
- [IE Driver Server](https://www.selenium.dev/documentation/ie_driver_server/) for Internet Explorer.
Selenium's support for a wide range of browsers makes it the most suitable tool for testing web applications on different browsers. The only downside is the requirement of downloading each browser and its webdriver.
**Playwright**: Like Selenium, Playwright supports multiple browsers including Firefox, Chromium-based browsers, and Safari using a single API. It provides a unified API for automating web browsers. This makes it an effective tool for cross-browser testing. Playwright defines this cross-browser testing behavior in a configuration file `playwright.config.js`. The content of the file responsible for the cross-browser testing looks is structured as shown below:
```js
module.exports = defineConfig({
/* Configure projects for major browsers */
projects: [
{
name: "chromium",
use: { ...devices["Desktop Chrome"] },
},
{
name: "firefox",
use: { ...devices["Desktop Firefox"] },
},
{
name: "webkit",
use: { ...devices["Desktop Safari"] },
},
/* Test against mobile viewports. */
{
name: "Mobile Chrome",
use: { ...devices["Pixel 5"] },
},
{
name: "Mobile Safari",
use: { ...devices["iPhone 12"] },
},
],
});
```
So once a user invokes a test using `npx playwright test`, Playwright executes the available tests automatically in all the browsers defined. After the tests are completed, it opens up a summary in the local browser to show the tests that passed and those that failed in all the respective browsers. The image below shows the browsers Playwright downloads during it’s installation process on Linux.

There are certain factors to consider when choosing the best Automated tool to use based on browser support, though any of the three can be used based on the preference of the user and the task at hand, it is important to note that of the three, Selenium is the most suitable Automated testing tool because it has such an extensive browser coverage,which includes older and less common versions of browsers. This feature distinguishes Selenium and makes it a better option based on browser support, In a situation where an application needs to be tested using a browser like Internet Explorer, Selenium is the only Automated testing tool among the three (Cypress, Selenium and Playwright) that supports Internet Explorer. This is not to say that Cypress and Selenium aren't also good options, In fact, Playwright also has an extensive browser support not just as much as Selenium. Cypress is more focused on Chromium-based browers and though it has limited browser support,it is the most suitable option for testing modern web applications in Chromium-based browsers.
| | Cypress | Selenium | Playwright | Winner |
| --------------- | ------- | -------- | ---------- | ---------------------- |
| Browser support | 4/5 | 5/5 | 5/5 | Selenium or Playwright |
### Choosing the best Automated testing tool based on Ease of Scripting
An Automated testing tool is controlled using a form of scripting. This scripting functionality can be implemented in a known programming language like Python or a custom domain-specific language. The tools in this article support different languages to different degrees. This section analyzes the ease of writing scripts for Automated testing with Playwright, Cypress, and Selenium.
**Cypress**: Cypress only supports scripting in Javascript and while this seems like an advantage to users that are JavaScript savvy, users that aren’t familiar with the JavaScript syntax will have to learn the language before getting productive writing tests with Cypress. As for the scripting API, Cypress makes it easy to easily write queries, assertions, and actions using methods such as `cy.get`, `cy.<element>.should`, and `cy.<element>.click`. `<element>` here refers to an element obtained from a [cypress query](https://docs.cypress.io/api/table-of-contents#Queries). The script below is a simple Automated testing script written for Cypress in JavaScript. It opens Google.com and searches for “cat memes”. It then verifies that the search was successful. Cypress’ simplicity enables this script to be written in 11 lines or less if you remove the describe block.
```javascript
describe("Search for cat memes on Google", () => {
it("visits google and searches for cat memes", () => {
cy.visit("https://google.com");
cy.get('textarea[name="q"]').type("cat memes");
cy.get('form[role="search"]').submit();
cy.title().should("contain", "cat memes");
});
});
```
**Selenium**: Selenium allows you to write scripts in multiple languages, from common scripting languages like Python and Javascript to more business oriented languages like Java and C#. Selenium supports multiple languages because it has a wide community of adopters and has been in existence the longest. Writing scripts in certain languages is easier than others partly due to the structure of the language, and the availability of well-maintained libraries and frameworks for Selenium in those languages. Find below the same script as the Cypress case that searches for cat memes on Google search implemented in JavaScript for Selenium.
```javascript
const { Builder, Browser, By, Key, until } = require("selenium-webdriver");
(async function testGoogleSearch() {
let driver = await new Builder().forBrowser(Browser.CHROME).build();
try {
await driver.get("https://www.google.com");
await driver.findElement(By.name("q")).sendKeys("cat memes", Key.RETURN);
await driver.wait(until.titleIs("cat memes - Google Search"), 1000);
} finally {
await driver.quit();
}
})();
```
**Playwright**: Similar to Selenium, Playwright supports more than one language. It has official support for [Javascript/Typescript, Python, Java, and .NET](https://playwright.dev/docs/languages). Its API is more page-oriented. This mean selectors (locators in this case) start from the `page` object, which is passed as an argument. Playwright’s JavaScript API focuses on human readability, making tests easier to write. It’s explicit use of the await syntax might seem verbose, but it makes it obvious that a task may take some time to complete. This flows with Selenium’s approach and differs from Cypress automatic await. The snippet below is code for searching for cat memes on Google Search, written for Playwright using JavaScript.
```javascript
import { test, expect } from "@playwright/test";
test.describe('Search for cat memes on Google"', () => {
test("visit google and searche for cat memes", async ({ page }) => {
await page.goto("https://google.com");
const searchBox = page.locator("textarea[name='q']");
await searchBox.fill("cat memes");
await searchBox.press("Enter");
await expect(page).toHaveTitle("cat memes - Google Search");
});
});
```
When it comes to Ease of Scripting, Selenium would have been the best pick because of it's support for multiple programming languages which allows users to write scripts in the language of their choice, but due to the complexity of Selenium's structure and it's rigid API, it might take a while for a beginner to totally understand Selenium as an Automated testing tool in contrast to tools like playwright and cypress which are beginner friendly and have simpler APIs. Playwright is the most suitable option based on Ease of Scripting because it is relatively easy to setup, it is beginner friendly, it supports some programming languages like JavaScript, Python, C# among others, it also has advanced built-in features like Network interception and Mobile emulation. Cypress is also a good option in terms of ease of scripting because it shares some features with Playwright, features like: User-friendly API, easy setup and built-in features, Cypress has only one Scripting language which is JavaScript and while this is an advantage to developers who have knowledge in JavaScript, it might be an issue to anyone who isn't familiar with JavaScript, Moreover, Cypress's main focus is chromium based modern web applications.
Here’s the summary of how the three testing tools rank up to each other:
| | Cypress | Selenium | Playwright | Winner |
| --------------------- | ------- | -------- | ---------- | ---------------------- |
| Browser support | 4/5 | 5/5 | 5/5 | Selenium or Playwright |
| Ease of scripting | 4/5 | 3/5 | 5/5 | Playwright |
### Choosing the best automated testing tool based on Ease of Setup
Similar to how a user will leave a website if it takes too long to load, a potential QA tester may abandon a tool if it is too difficult to set up. Fortunately, none of the testing tools in this guide are difficult to set up. However, you should have in mind which of these tools is the easiest to set up.
**Cypress**: Cypress comes as an npm package and a [standalone downloadable application](https://docs.cypress.io/guides/getting-started/installing-cypress#Direct-download) that you can immediately install and write tests with. After installation, you only add a new project, choose a browser of choice, and start writing test cases in JavaScript.

Setting up Cypress as an npm package is equally straightforward. You add it to your project using `npm install cypress --save-dev` and start up the application using `npx cypress open`. From there, you can skip the project initialization and go straight to picking a browser and running example tests or writing new ones.
**Step by step guide to setting up Cypress**:
Step 1: Download Nodejs: Go to your search engine and search for nodejs download. Click on the result and you will be directed to a page where you can select the version of nodejs suitable for the operating system of your laptop. Then click on the download button.
Step 2: After you have successfully downloaded nodejs, a welcome page will be displayed, follow all due instructions and click on next till you are directed to click on the install button, it only takes a few seconds at most.

Step 3: Download Visual studio code: After visual studio code has been downloaded, you will be prompted to follow certain instructions to successfully install it.
Step 4: Create a new folder to set up your cypress tests. You can name it 'Cypress Automation'.
Step 5: After you have successfully created a folder. Go to VS Code and click on 'File', after you click on file, click on 'Open folder'. you should be directed to the location where the folder was created, then click on 'select folder'
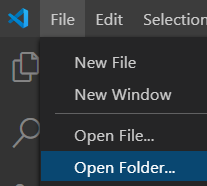
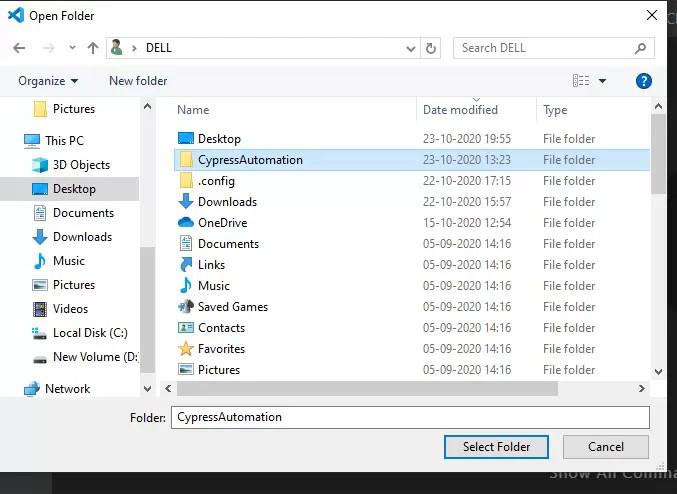
After you have clicked on 'Select folder', this window should come up:
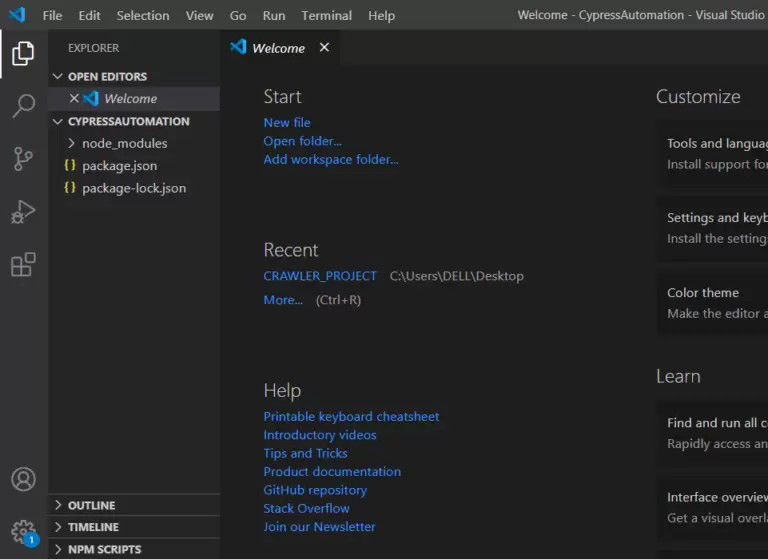
Step 6: Run the command 'npm init' on your vs code terminal.
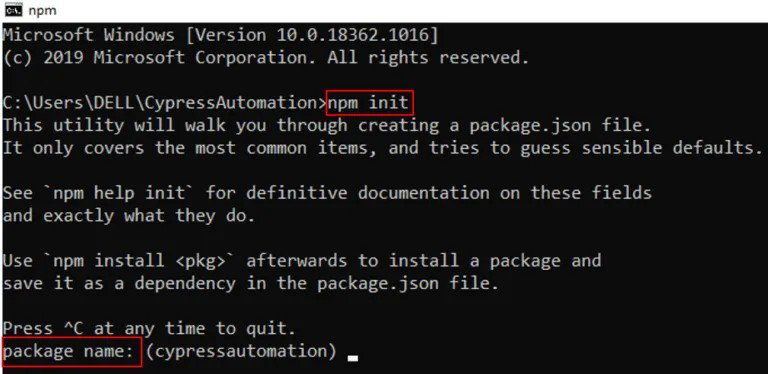
Step 7: After that, run the 'npm install' command to install cypress
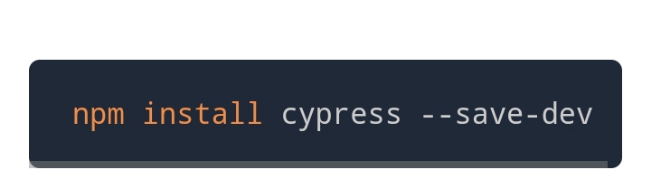
Step 8: To open cypress, run the command below

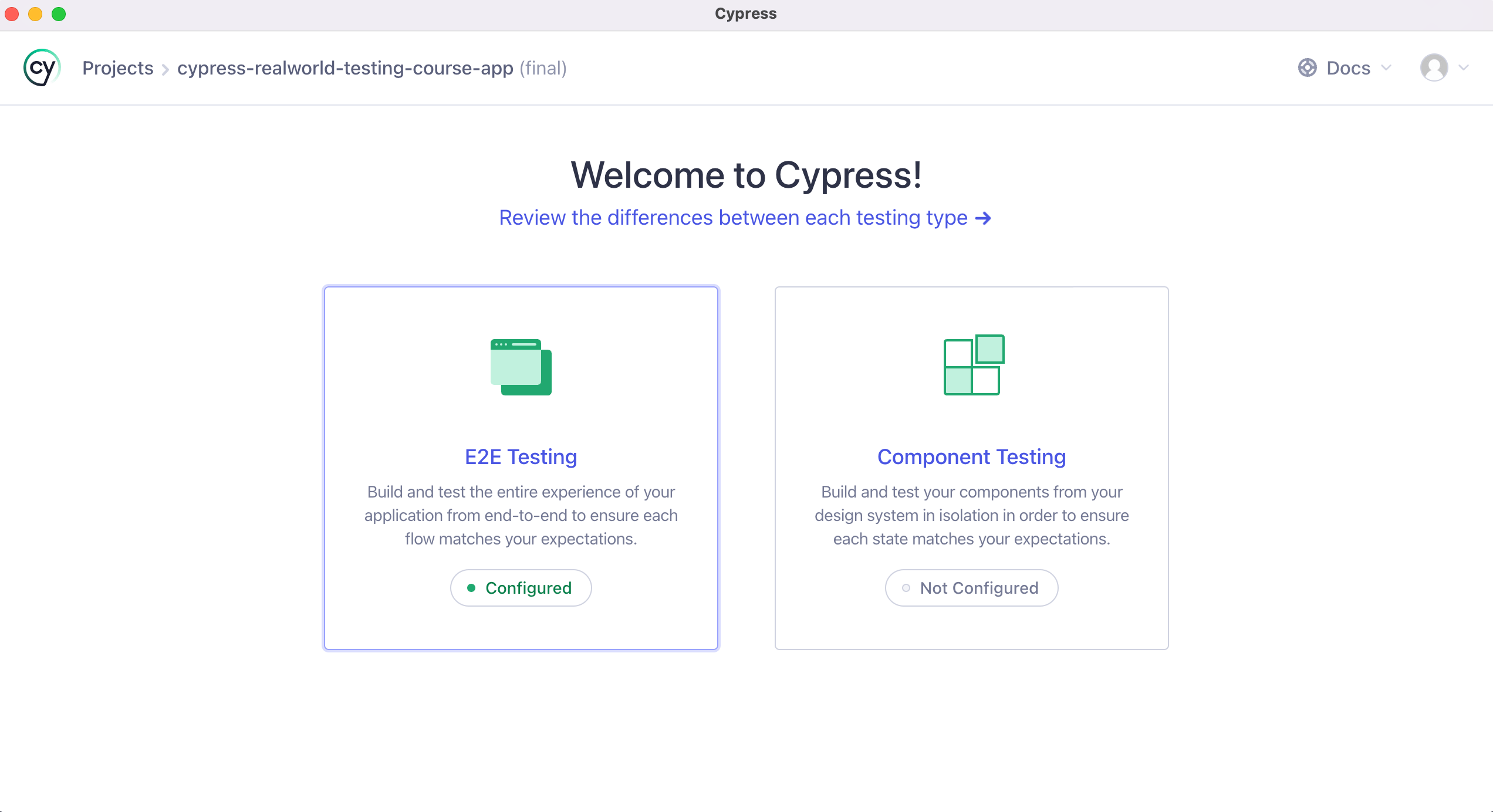
Step 9: If you have followed all the steps correctly, you should be directed to the page shown in the image below
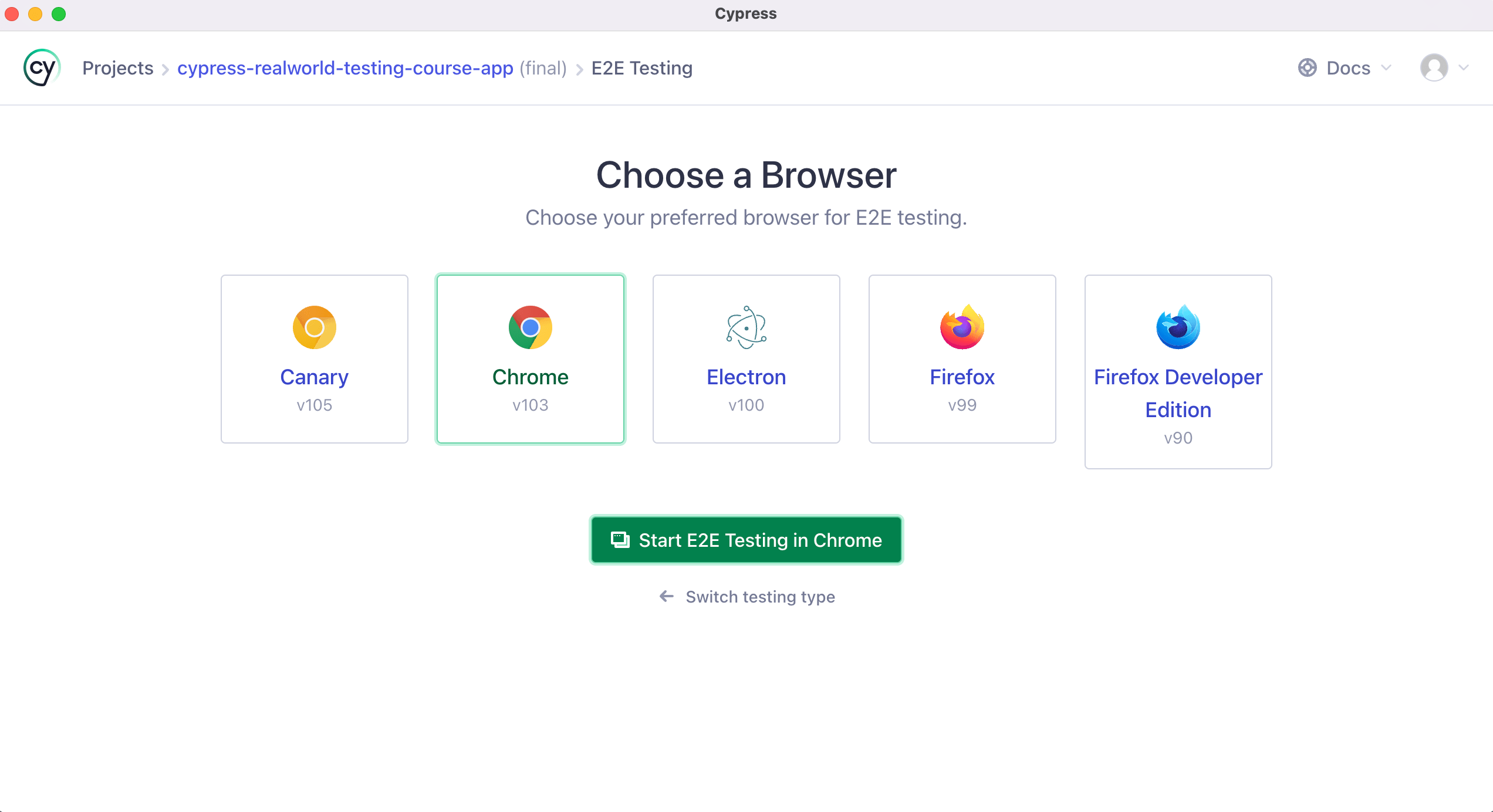
Step 10:After you have clicked on the browser of your choice, Click on the 'Create new spec' option
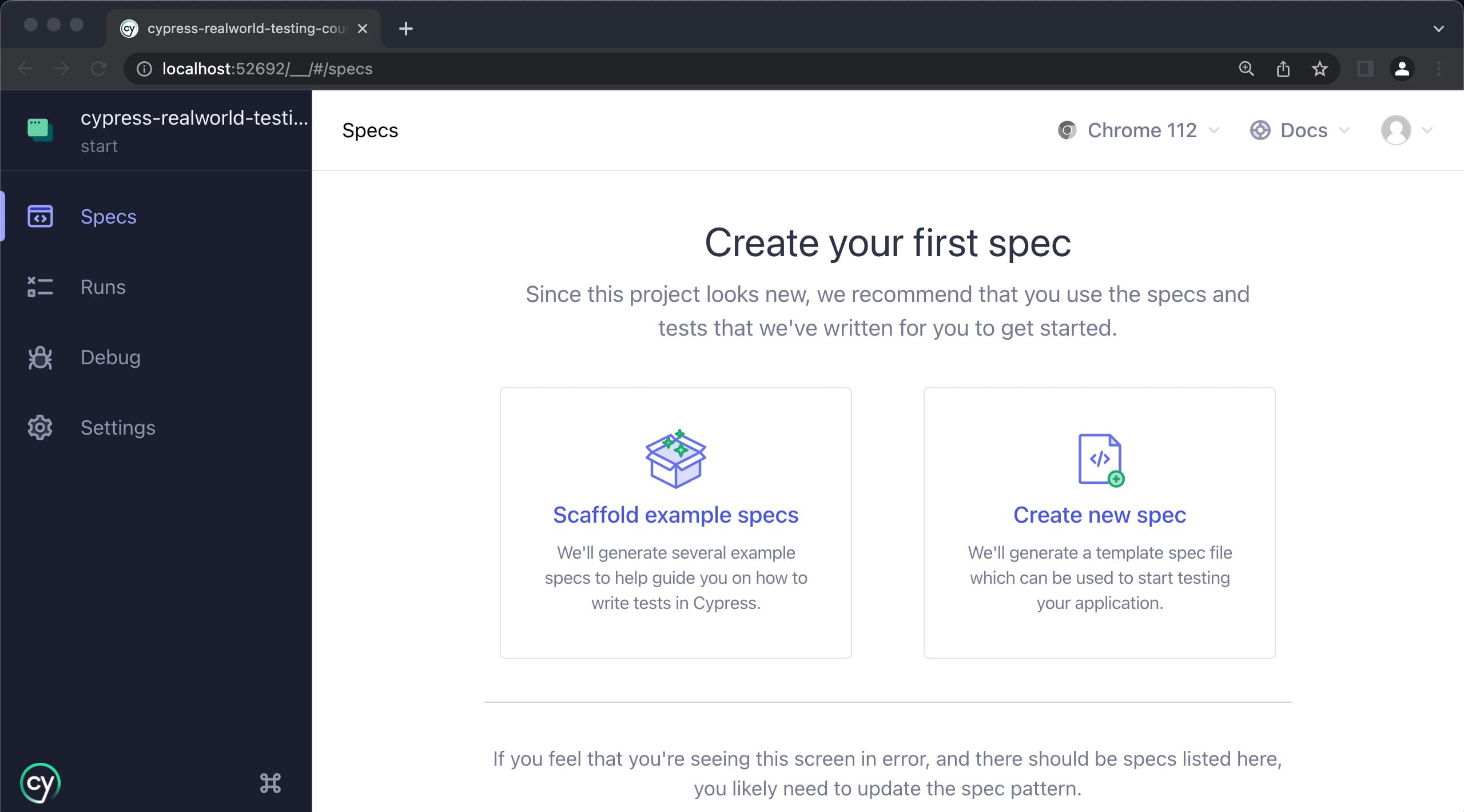
Step 11: After the image below is displayed, click on create spec
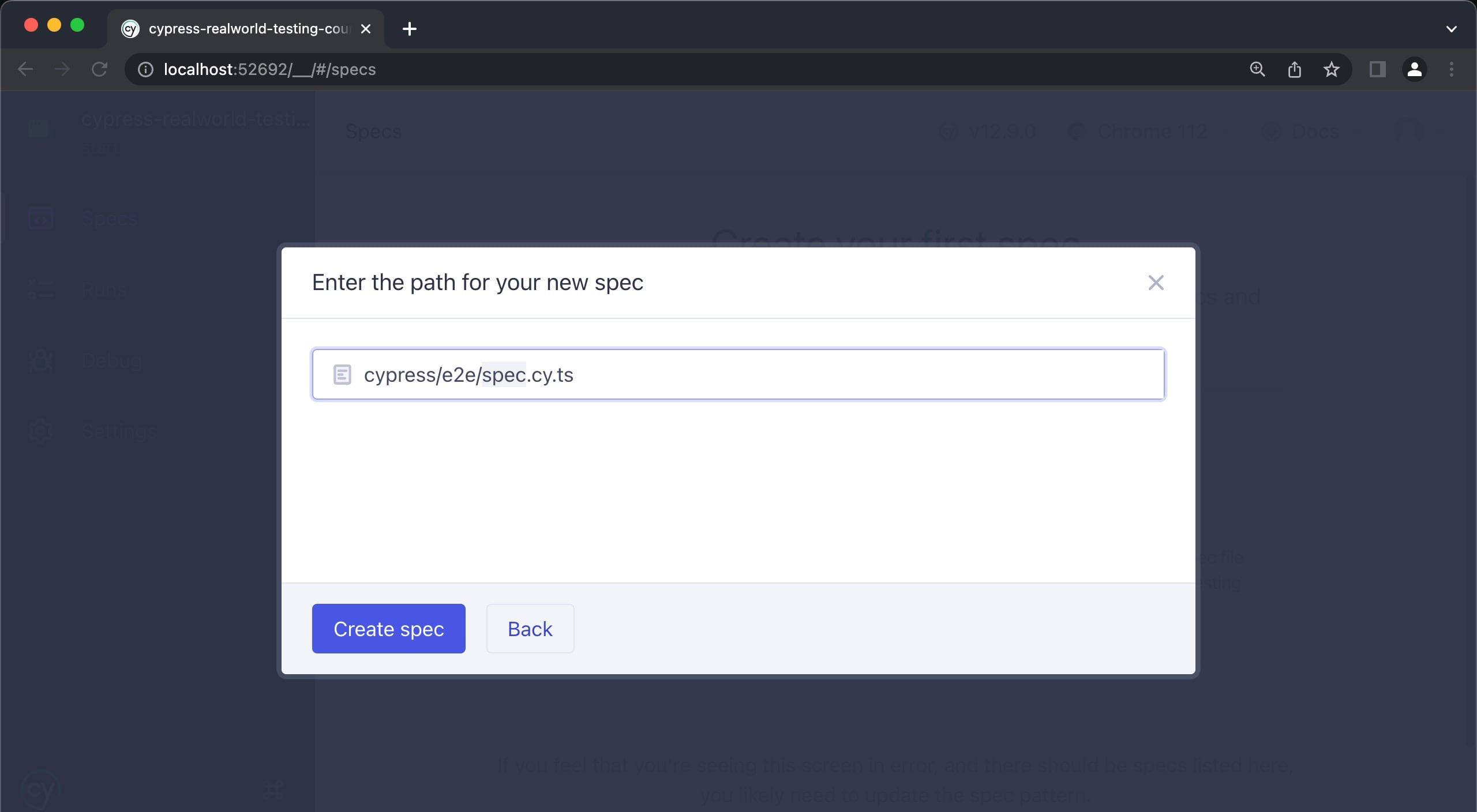
Step 12: Click on 'ok, run the spec'
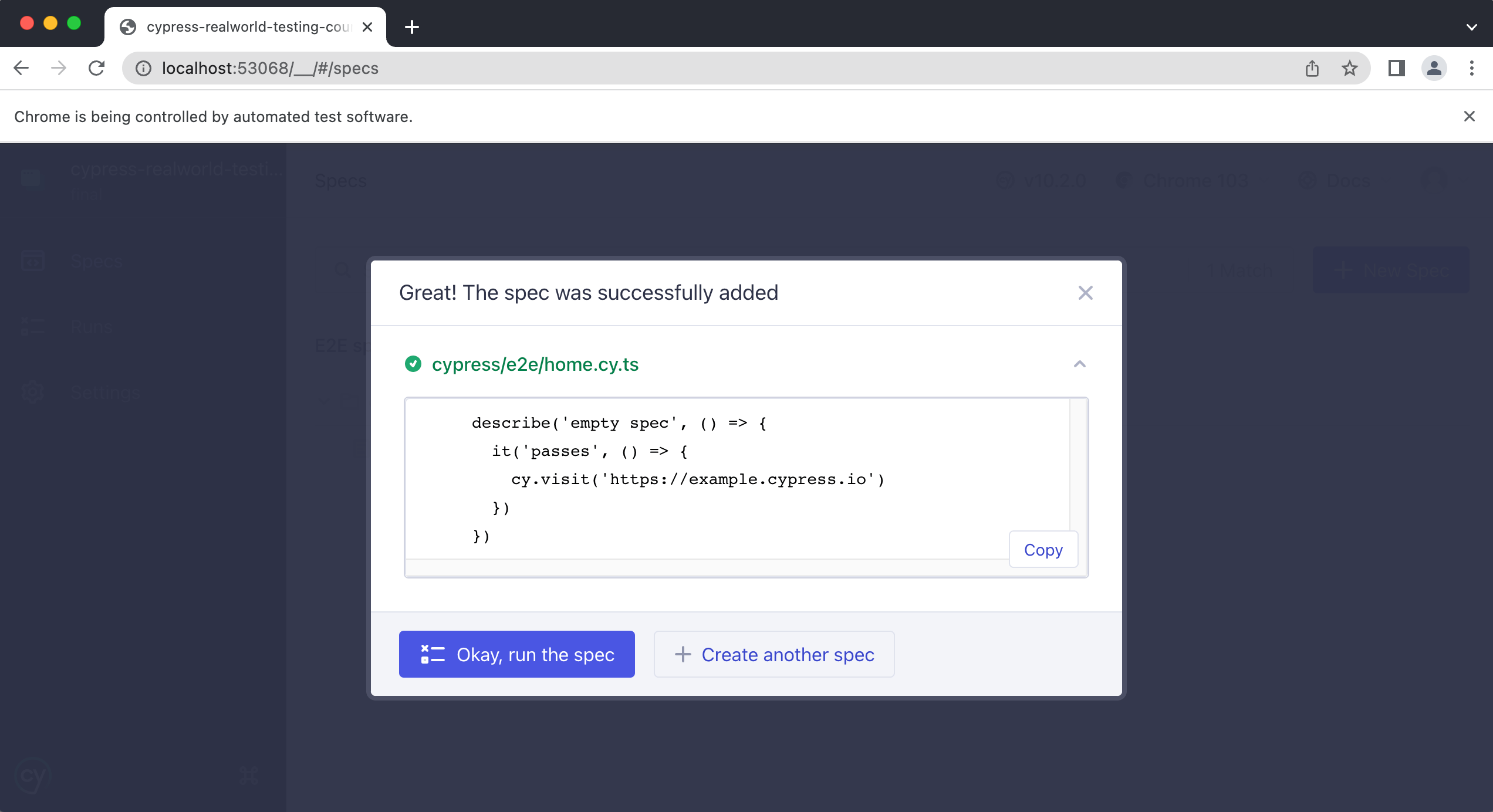
Step 13: There you have it, your first successful cypress test!
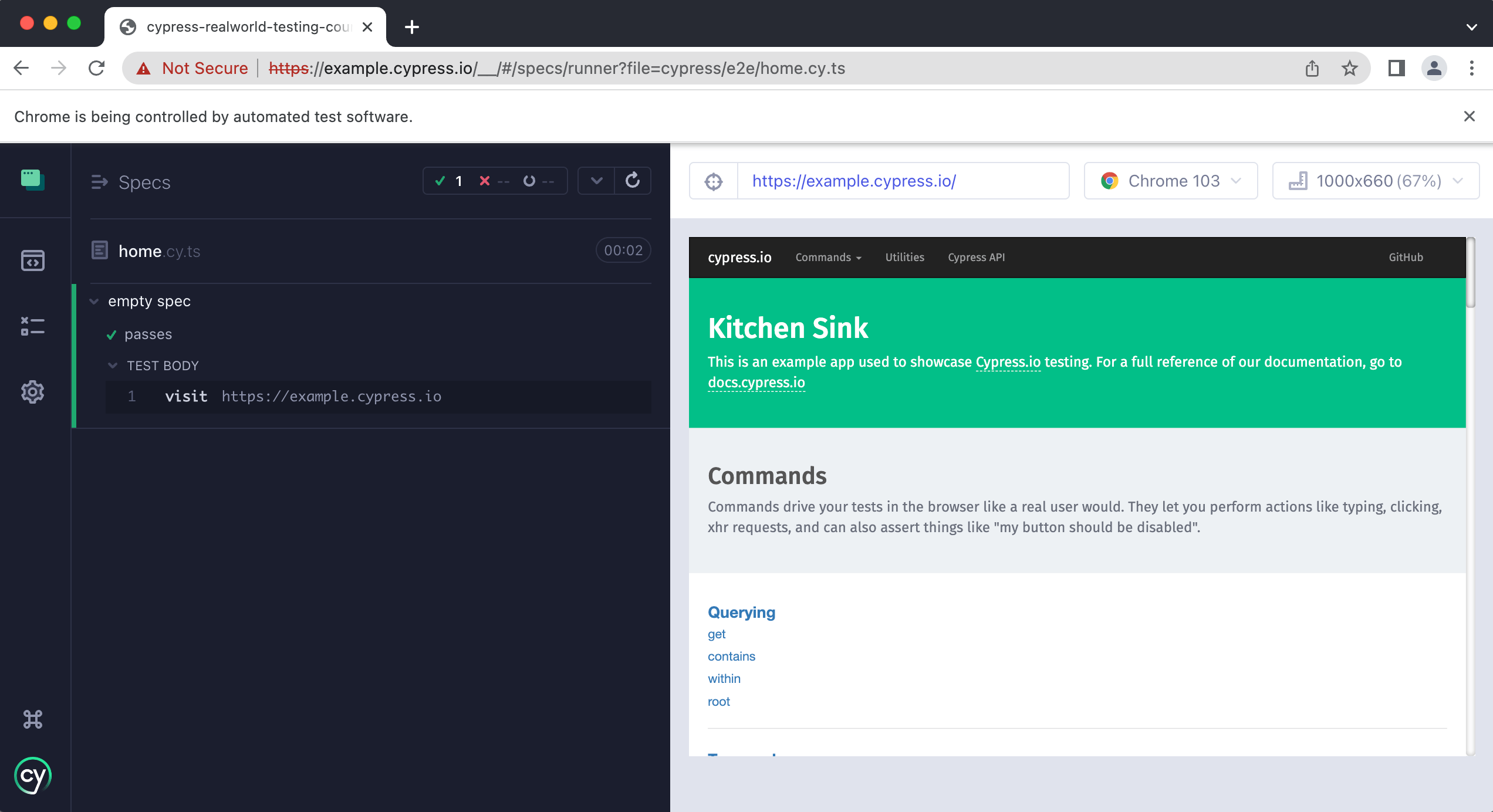
>**Please Note**: If you are experiencing issues during the installation process, Check Cypress's Official Documentation: [Cypress Documentation ](https://docs.cypress.io/guides/overview/why-cypress)
**Playwright**: Playwright is set up from the command line, using an npm command: `npm init playwright`. This initialization step is an interactive workflow that asks you to choose your desired scripting language (Javascript or Typescript), the location of your test scripts, and whether to include a Github Actions Workflow for CI.
After these prompts, you can write new tests or run existing example tests using the command: npx Playwright test. Playwright also includes a UI mode that is accessed using the `--ui` flag when invoking it using npm.

Aside from Playwright’s dependency on Node.js, it simplifies browser setup/connection by downloading the required testing browsers in the local directory. This means that even if you do not have the required browsers installed, you can still run Playwright tests.

**Step by step guide to installing playwright**:
The installation process of Playwright is somewhat similar to that of Cypress and if you have followed the Cypress installation steps carefully, then this process should be an easy one for you.
Step 1: Install Visual studio code.
>If you have installed Visual Studio Code, you can skip this step. If you haven't, click on this link below:
[Visual studio code](https://code.visualstudio.com)
Step 2: Create a new Folder.
Step 3: Search for playwright extension in Visual Studio Code and install it.
Step 4: Search 'Playwright' and click on Test: Install Playwright
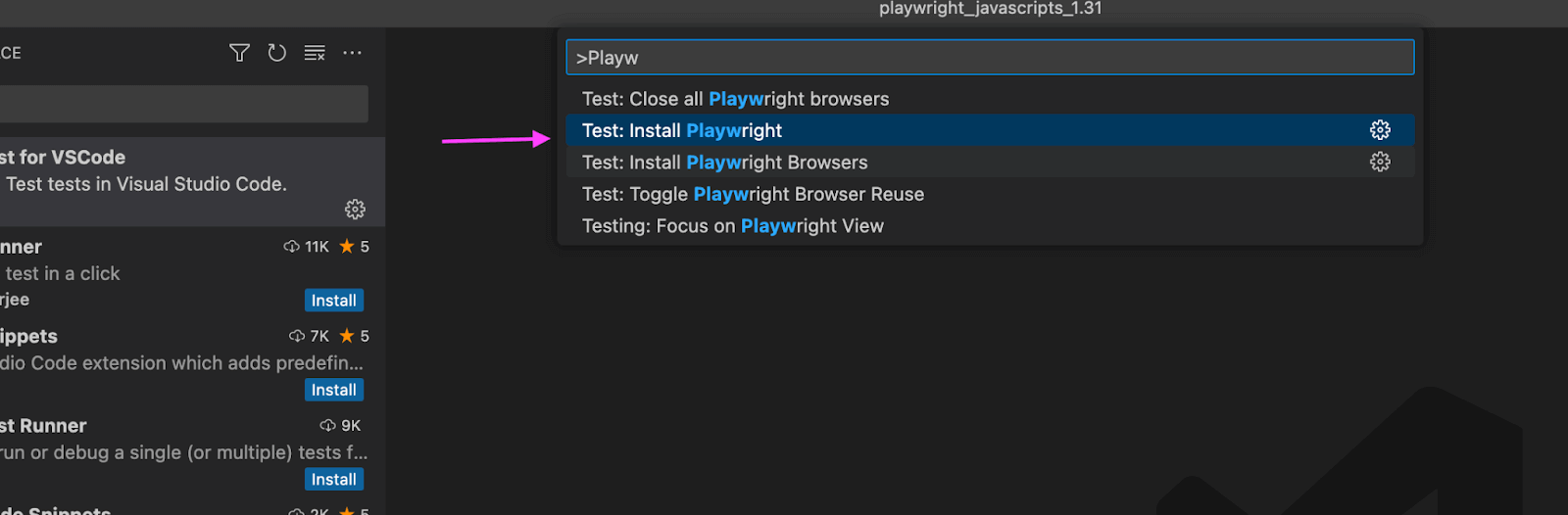
Step 5: Finally, click the ok button
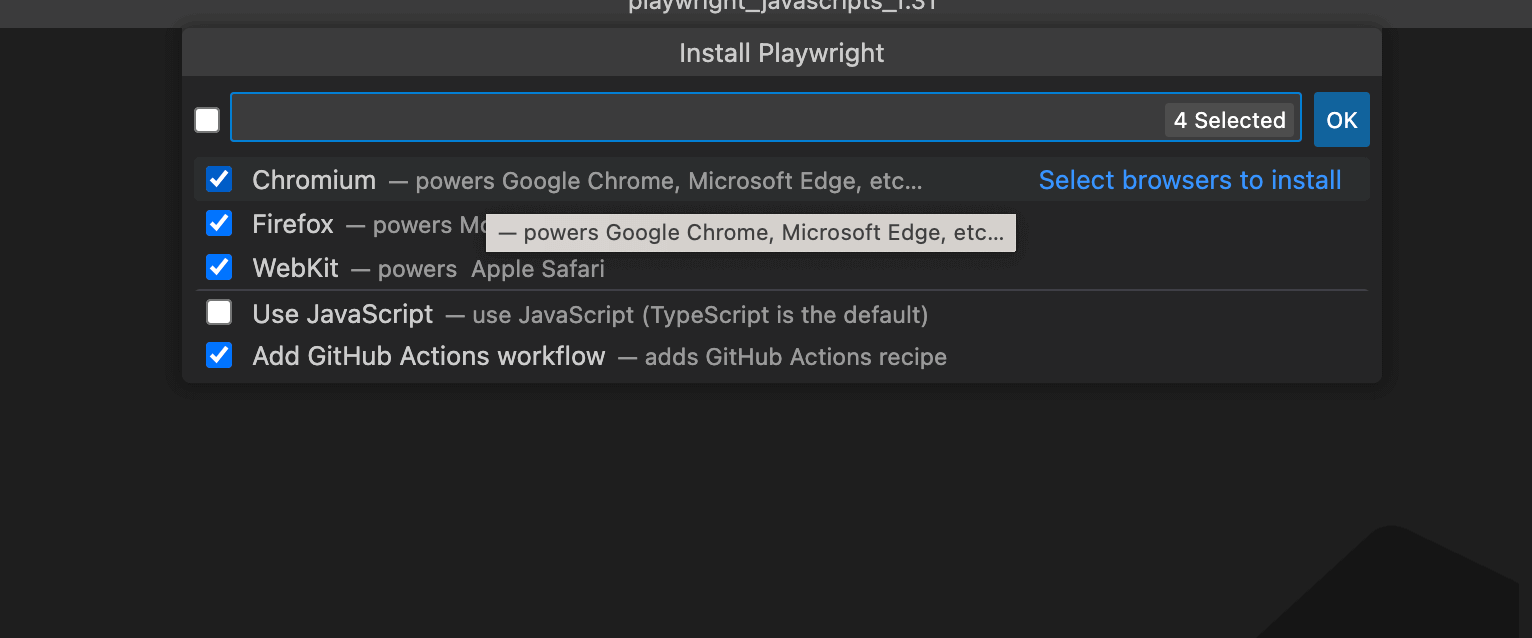
Just like that, you are done!
>**Please Note**: If you are experiencing difficulty with the installation process. Check the official documentation: [Playwright's official documentation](https://playwright.dev/)
**Selenium**: Selenium has the most involved setup among the three tools. For starters, you need to have the drivers for the browsers you want to test with. So if you wish to test your applications with Chrome and Firefox, you will need to have both browsers installed alongside their Selenium webdrivers. This tedious setup process can be abstracted by the client library, giving you a straightforward way of running your tests. However, this convenience is not present in all Selenium client libraries.
**Step by step guide to installing Selenium**:
There are four main steps to installing Selenium. They are:
Step 1: Download and Install Java. Go to the official java website.
[Java Installation](https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/downloads/)
Step 2: Set up the environment variable:
* Go to your pc setting and click on advanced system setting.

* Click on environment variable button
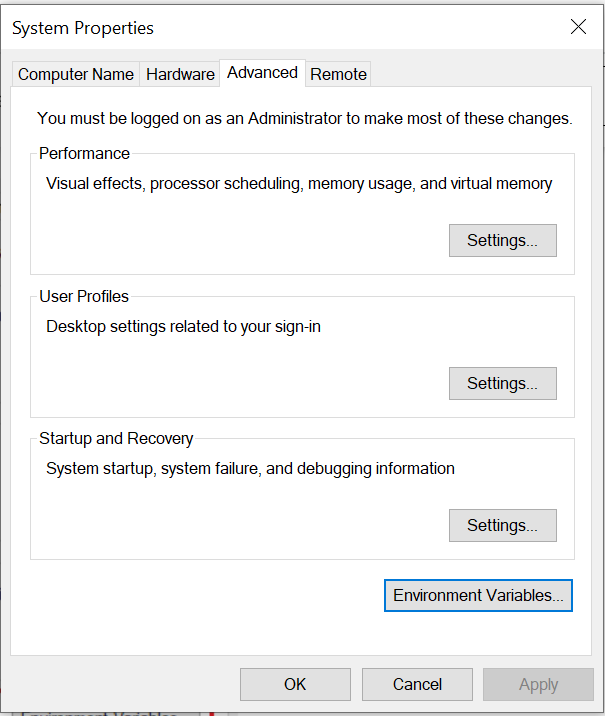
* Under system variable, select path and click on edit button. Now set the complete java path and click on save.
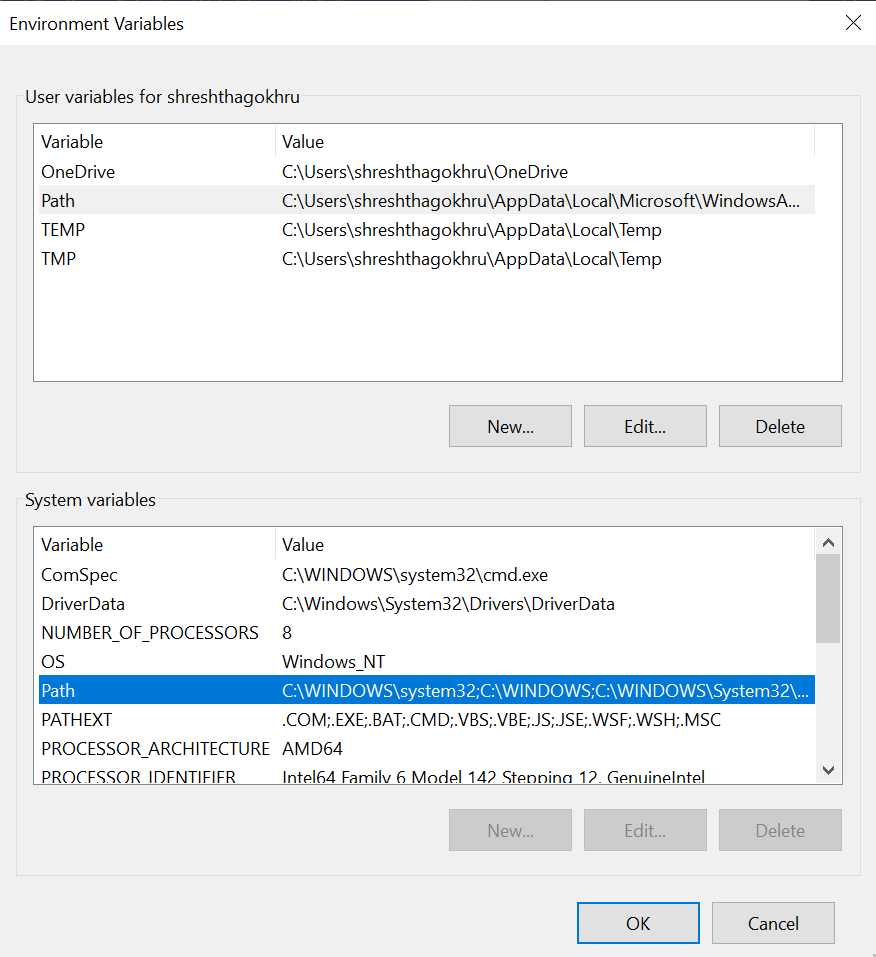
* Download and install selenium client and webdriver languages from the Selenium website and extract the down
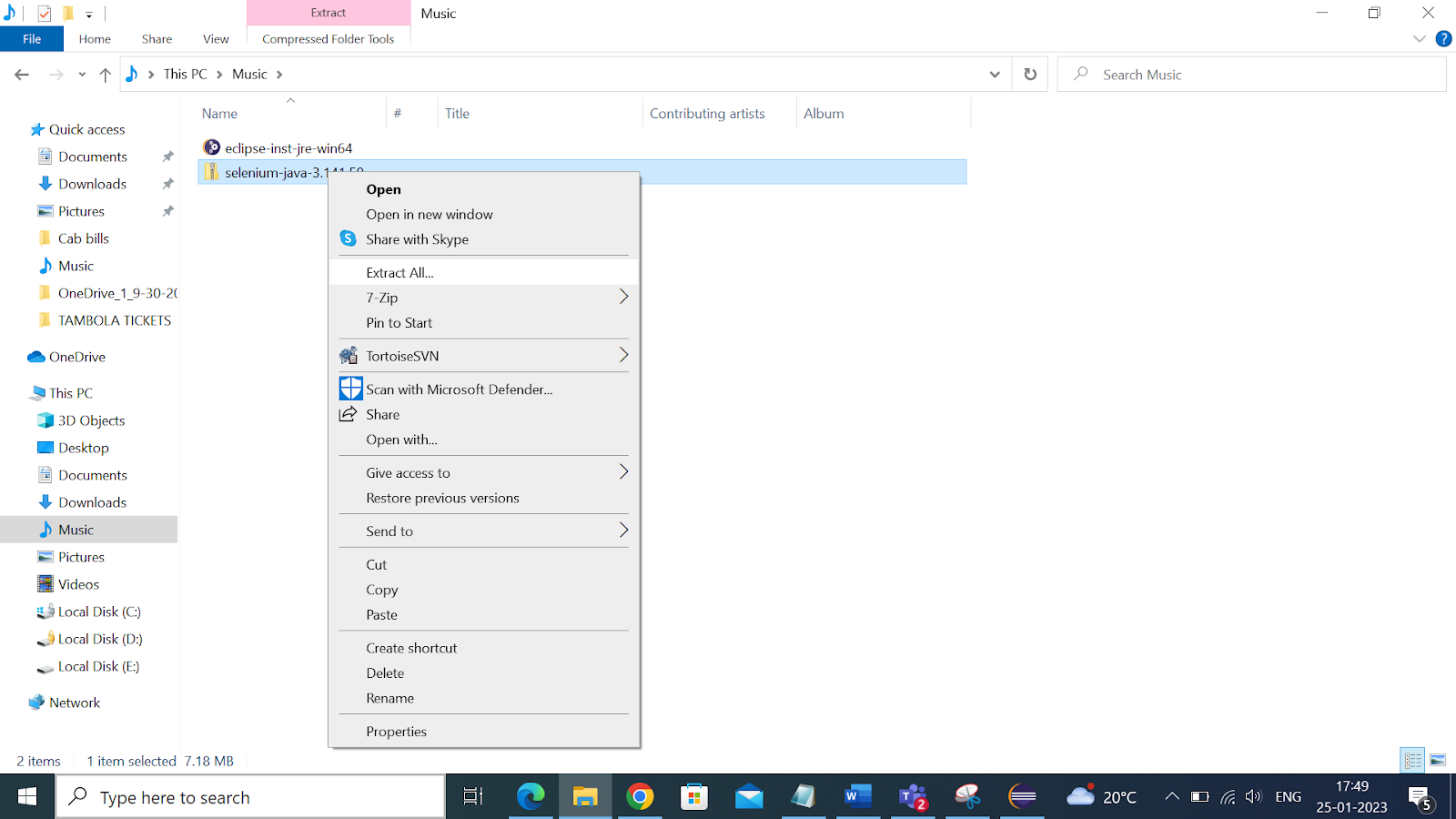
It should look like this:
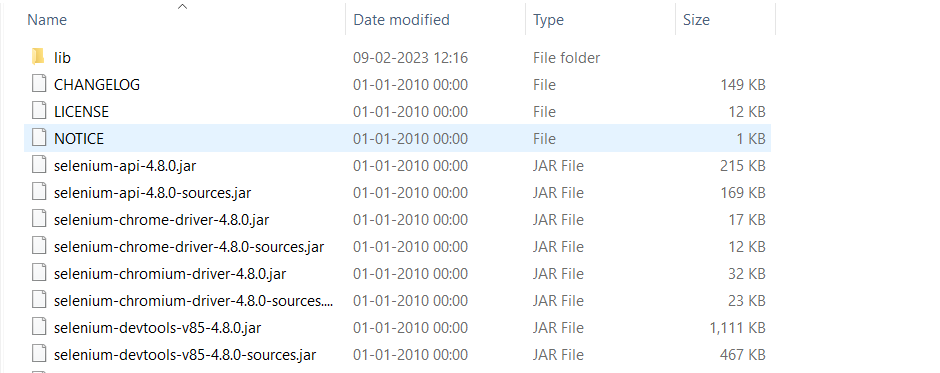
Step 3: Install webdrivers:
Now, you have to install webdrivers for specific browsers because it is necessary for Selenium to interact with that browser. Since Chrome is a very popular web browser. Use this link [chrome driver](https:// "chromedriver.chromium.org/downloads") to download the chrome web driver. Once you have downloaded it, add the path of the downloaded driver to your system environment variable.
Step 4: Download and install Eclipse for Selenium webdriver
* Go to the official Eclipse website Eclipse website and download Eclipse
* Once the download is complete, unzip the archive and extract the content to a directory on your computer
* Now you need to create a workspace to store your test scripts and test results.
* Click on the launch button and your installation is complete.
>>**Please Note**: If you are experiencing difficulty with the installation process,Check Selenium's official Documentation: [Selenium's official Documentation](https://www.selenium.dev/documentation/)
Here’s the summary of how the three testing tools rank up to each other:
| | Cypress | Selenium | Playwright | Winner |
| --------------------- | ------- | -------- | ---------- | ---------------------- |
| Browser support | 4/5 | 5/5 | 5/5 | Selenium or Playwright |
| Ease of scripting | 4/5 | 3/5 | 5/5 | Playwright |
| Ease of set up | 5/5 | 2/5 | 4/5 | Cypress
|
### Choosing the best automated testing tool based on Performance and Speed
It's important to think about how well an automated testing tool works and how fast it is before picking one. This helps in making sure the tool fits with what the project needs, what the team can handle, and the project's long-term goals.
**Cypress**: Cypress is generally known for its faster-than-average execution time. This is most likely the case because it executes commands inside the target browser. It doesn't use an external driver like Selenium does but injects JavaScript code into the browser. The injected code then does all the DOM node parsing and manipulation to achieve the testing goal. Also, Cypress provides a feature called Parallelization. This feature allows Cypress to execute many tests simultaneously. While Selenium also supports parallel test execution, Cypress' direct test execution model makes it faster.
**Selenium**: Selenium's architecture, which relies on a driver for different browsers adds a lag to its test execution speed and performance. This dependency on drivers does not exist for both Cypress and Playwright. Selenium works by creating a separate driver instance for each browser session. So if a user tries to execute tests in parallel, Selenium will create as many web driver instances as browsers involved. This architecture puts Selenium behind Cypress and Playwright despite its versatility.
**Playwright**: Like Cypress, Playwright offers fast execution by leveraging its unified API feature. Playwright by default runs tests on Chromium, Firefox, and Webkit. It can do this because it installs these browsers during its installation process. Playwright does not fail when tests are flaky because it ensures that elements are visible before proceeding with tests. Playwright’s major contender when it comes to Performance and speed is Cypress because it has a similar simplified architecture. Both Playwright and Cypress have Node.js as a dependency, unlike Selenium that has a broader community of supported frameworks.
Based on Speeed and performance, Selenium is far behind Playwright and Cypress due to it's complicated Architecture and it's dependence on webdrivers to interact with browsers, this two factors greatly impacts Selenium's speed and performance. Of the three tools, Playwright is the best Automated testing tool based on speed and performance due to its Modern Architecture, ability to perform parallel testing which allows it to run multiple test cases simultaneously across different browsers. Playwright also records high execution speed in scenarios where complex test cases are being executed, this puts it above Cypress because even though Cypress also records high execution speed, this only applies to testing that involves Chromium based browsers.
Here’s the summary of how the three testing tools rank up to each other:
| | Cypress | Selenium | Playwright | Winner |
| --------------------- | ------- | -------- | ---------- | ---------------------- |
| Browser support | 4/5 | 5/5 | 5/5 | Selenium or Playwright |
| Ease of set up | 5/5 | 2/5 | 4/5 | Cypress |
| Ease of scripting | 4/5 | 3/5 | 5/5 | Playwright |
| Performance and speed | 4/5 | 3/5 | 5/5 | Playwright
## Conclusion
Choosing the most suitable Automated testing tool is a very essential step that all developers and testers must take into consideration before kickstarting the process of testing a software product. Below are key things to take into consideration before choosing an Automated testing tool:
* You must consider the task at hand and the skillset of whoever is carrying out the test. For example, if a tester is very knowledgeable in JavaScript, choosing Cypress as an Automated testing tool will be a good option because they will encounter little to no difficulty while executing test cases.
* Unless there is need to execute test cases using a very old or less common version of a browser, Playwright or Cypress are better options compared to Selenium.
* Before choosing any Automated testing tool to execute test cases, Make sure that there is actually a need to carry out that particular test using an Automated testing tool. Automated testing is not a replacement for Manual testing.
>**Please Note**: Always check the official documentation of any Automated testing tool for clairity on whatever issues you may encounter either during the installation process or while using the tool.
You must carefully consider all these factors before choosing an Automated testing tool to prevent difficulty while testing, So while all these tools may be robust with good community support, you should always choose a tool that closely matches your use-case.
>**For further reading, Click on the links provided below**:
[Selenium vs Playwright vs Pupeteer: A comparison](https://www.browserstack.com/guide/cypress-vs-selenium-vs-playwright-vs-puppeteer)
[Selenium vs playwright vs cypress: A comparison](https://www.lambdatest.com/blog/playwright-vs-selenium-vs-cypress/)
[Selenium vs playwright vs Cypress](https://zebrunner.com/blog-posts/selenium-vs-cypress-vs-playwright-comprehensive-comparison)
# General Review
## SEO Analysis
### Meta Description
- **Current Meta Description**: Missing
- **Suggested Meta Description**: "Compare Cypress, Selenium, and Playwright to find the best automated testing tool for your frontend web applications. Discover the strengths and weaknesses of each tool."
### Keywords
- **Current Keywords**: Not provided
- **Suggested Keywords**: Cypress, Selenium, Playwright, automated testing tools, frontend testing, e2e testing, browser support, scripting ease, performance.
>NOTE: Please incorporate these keywords naturally in the content
### Header Tags
- Ensure all headers (H1, H2, H3) are used appropriately and contain target keywords.
- Example: "## What is Automated testing?" can be "## What is Automated Testing and Why is it Important?"
## Grammar and Style Analysis
### Introduction
- **Current**: "Automation testing is a software testing paradigm where tests are run automatically using a tool or a script."
- **Suggested**: "Automation testing is a software testing methodology where tests are executed automatically using tools or scripts."
### Consistency
- Ensure consistent use of capitalization, especially for tool names like "Cypress", "Selenium", and "Playwright".
### Active Voice
- Use active voice for a more engaging tone.
- Example: "The testing tool used in automated testing has two major components, a test runner and a tracking agent." should be "Automated testing tools have two major components: a test runner and a tracking agent."
### Clarity
- Break down complex sentences to improve readability.
- Example: "The purpose of this comparison is to enlighten you on the best tool for your use-case based on the mentioned metrics." can be "This comparison aims to help you choose the best tool for your use-case based on metrics like browser support, language support, ease of setup, and performance."
## Structure and Formatting
### Sections
- Ensure each section has a clear heading and flows logically from one to the next.
### Bullet Points
- Use bullet points for lists to improve readability.
- Example: The benefits of automated testing should be in bullet points.
### Code Blocks
- Ensure code blocks are formatted correctly and include language-specific syntax highlighting. You can use the online prettier formater.
- Example:
```javascript
describe("Search for cat memes on Google", () => {
it("visits google and searches for cat memes", () => {
cy.visit("https://google.com");
cy.get('textarea[name="q"]').type("cat memes");
cy.get('form[role="search"]').submit();
cy.title().should("contain", "cat memes");
});
});
```
### Callouts
- Use callouts for important information, tips, and notes.
- Example:
> **Note**: For local development, use [SMEE](https://smee.io) as a webhook relay to facilitate communication between MUX and your locally hosted Strapi instance.
## Content Enhancement
### Introduction Expansion
- Provide more context on the importance of automated testing and its benefits.
### Detailed Comparisons
- Expand on the comparison metrics with practical examples and benefits.
- Example: Provide specific scenarios where one tool might be preferred over the others.
### Setup Guide
- Provide a step-by-step guide with screenshots for setting up each tool.
### Conclusion
- Summarize key takeaways and encourage readers to choose the tool that best fits their needs.
- Provide links to additional resources and community forums.
## Final Review
After addressing the above points, the blog post will be more optimized for SEO, easier to read, and provide greater value to the readers.